Are you wondering what wavelengths power your solar panels?
Keep reading for easy-to-understand answers. Let’s dive into the wavelengths that make it all work.
What light spectrum or wavelengths do solar panels use?
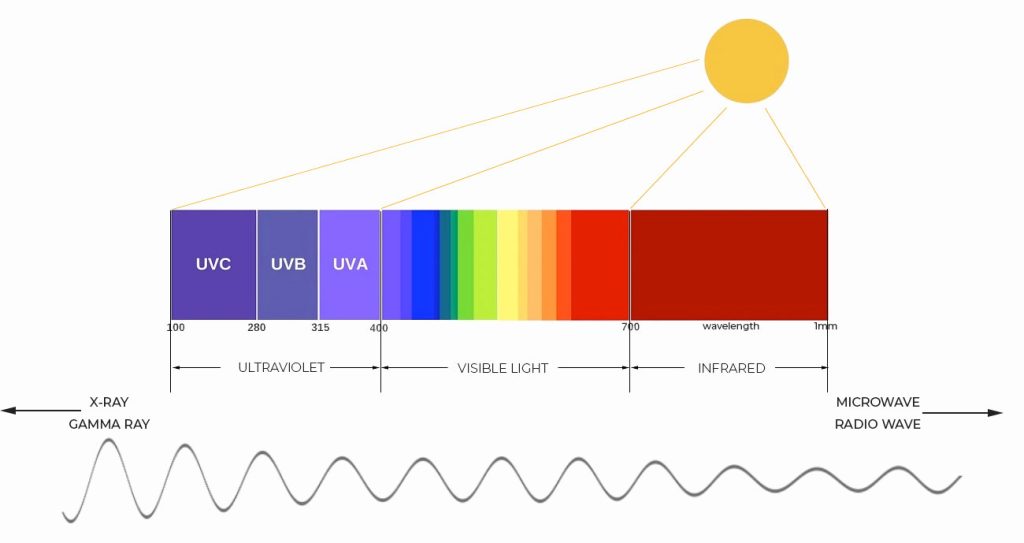
Solar panels primarily utilize the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum known as the “solar spectrum” or “solar irradiance.”
The Sun emits a broad range of electromagnetic waves, and solar panels are designed to capture and convert a specific range of wavelengths into electricity. If you’re interested in the details of this process, check out our blog post on solar energy.
The key region for solar energy is in the visible and near-infrared part of the spectrum.
1. Visible Light
- Solar panels are most efficient in converting visible light into electricity. This includes wavelengths roughly between 400 and 700 nanometers.
- Photovoltaic cells, the building blocks of solar panels, are particularly responsive to the blue and red parts of the visible spectrum.
2. Near-Infrared
- Some solar panels are designed to capture light in the near-infrared range, which extends beyond the visible spectrum (wavelengths longer than 700 nanometers).
- Although less efficient than visible light absorption, capturing near-infrared light allows solar panels to utilize a broader range of sunlight.
3. Ultraviolet (UV) Light
- Solar panels also receive ultraviolet (UV) light from the Sun, but the energy in this part of the spectrum is typically lower.
- While some solar technologies can harness UV light, the overall contribution to energy conversion is relatively small compared to visible and near-infrared light.
Most of the energy in sunlight is concentrated in the visible part of the spectrum. A silicon cell, commonly used in solar panels, has a cutoff of 1100 nanometers. This means that it won’t absorb any energy with wavelengths larger than this.
Engineers and scientists continuously work on improving solar panel efficiency, exploring materials and technologies to extend the range of wavelengths that can be effectively captured for energy conversion.
Can Solar Panels Use Ultraviolet or Infrared Light?
Yes, solar panels can use ultraviolet and infrared light.
As stated above, solar panels efficiently convert visible light and capture near-infrared light. While ultraviolet contributes, it’s less efficient.
Silicon-based panels have a cutoff at 1100 nm, limiting absorption beyond this point. Ongoing research aims to broaden the spectrum for improved efficiency.
Do solar panels absorb light or heat?

Solar panels primarily absorb light, not heat.
1. Primary Absorption
- Solar panels primarily absorb light rather than heat.
- The photovoltaic cells within the panels are designed for the photovoltaic effect.
- This process involves the absorption of photons (light particles) from sunlight.
2. Photovoltaic Effect
- Photons striking the semiconductor material in solar cells excite electrons.
- This excitation creates an electric current that is harnessed as electricity.
3. Heat Impact
- Solar panels are not designed to absorb heat directly.
- Excessive heat can sometimes decrease the efficiency of solar panels.
- Some solar technologies incorporate cooling mechanisms to manage temperature and optimize performance.
It’s crucial to understand that the absorption in solar panels is primarily focused on light to generate electricity, and the impact of heat on panel efficiency is managed through specific design considerations.
Is there a way to make my solar panels more efficient?

Yes, there are several strategies to potentially increase the efficiency of solar panels.
Here are some tips:
- Optimal Placement:
- Ensure that your solar panels are correctly positioned to receive maximum sunlight throughout the day. This may involve adjusting the tilt angle and orientation.
- Regular Cleaning:
- Keep the solar panels clean from dust, dirt, and debris. Regular cleaning helps maximize light absorption.
- Trim Surrounding Vegetation:
- Trim any nearby trees or vegetation that may cast shadows on the solar panels, as shadows can reduce overall efficiency.
- Use of Reflective Surfaces:
- Consider incorporating reflective surfaces around the solar panels to redirect additional sunlight onto them.
- Advanced Technologies:
- Explore advanced solar panel technologies, such as bifacial panels or concentrated solar power systems, which can increase overall energy capture.
- Cooling Systems:
- Some systems incorporate cooling mechanisms to manage temperature, enhancing efficiency, especially in hot climates.
- Upgrading Inverters:
- Upgrading inverters can improve the efficiency of energy conversion and maximize the electricity generated.
- Battery Storage:
- Integrate energy storage solutions, like batteries, to store excess energy for later use, making your overall energy usage more efficient.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Conduct regular maintenance checks to identify and address any issues promptly.
It’s essential to consult with a professional or manufacturer before implementing changes to ensure they are compatible with your specific solar panel system.
Conclusion
Armed with insights into the wavelengths that power your solar panels and our helpful list on optimizing efficiency, you’re ready to take charge of your solar setup.
Apply these insights today and let your solar panels shine at their brightest!