Have you ever wondered how those slim thin-film solar panels work and if they’re right for your energy needs?
Well, you’re about to find out! This guide breaks down the science behind those sleek panels, making it easy for you to decide if they’re a fit.
What are thin-film solar panels?
Understanding Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels represent a unique photovoltaic technology, employing materials like
- amorphous silicon (a-Si)
- cadmium telluride (CdTe)
- or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)
These panels are characterized by their distinctive manufacturing process, setting them apart from traditional crystalline silicon panels.
Efficiency Evolution
Historically, thin-film solar cells had lower efficiency compared to crystalline silicon counterparts.
However, advancements in technology have elevated their output, placing them on par with other available solar options.
Manufacturing Advantage
Thin-film solar cells stand out as the easiest and fastest solar panel type to manufacture. This advantage in the production process contributes to their widespread use in various applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Break-Even
Their lower initial cost is a key factor in the popularity of thin-film panels. This cost advantage enables a faster break-even point in investments compared to poly or monocrystalline panels.
Considerations for Longevity
While offering a faster return on investment, it’s essential to note that thin-film panels typically have a lifespan of 10-20 years.
This makes them a practical but shorter-term investment compared to the longevity of other solar options.
Ideal Applications
Given their characteristics, thin-film solar panels are well-suited for specific applications, including large-scale solar farms, building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), and scenarios where rapid deployment and adaptability are paramount.
How many watts does a thin film solar panel produce?
On average, thin-film solar panels produce fewer watts per square meter compared to crystalline silicon panels.
The typical power rating for thin-film panels is less than 200 watts.
What are the advantages of thin film solar panels?

Cost-Effectiveness
Thin-film panels are generally more cost-effective to produce, making them an attractive option for large-scale installations where initial investment is a crucial factor.
Lightweight and Flexible
The thin and flexible nature of these panels allows for versatile installation options, making them suitable for unconventional surfaces or temporary applications.
Rapid Manufacturing
Thin-film technology is the fastest and easiest to manufacture among solar panel types, contributing to quicker production times and potential cost savings.
Adaptability to High Temperatures
Thin-film panels may perform relatively better in high-temperature environments compared to crystalline silicon panels, as they can handle heat more effectively.
What are the disadvantages of thin film solar panels?

Lower Efficiency
Thin-film panels generally have lower efficiency compared to crystalline silicon panels, meaning they convert sunlight into electricity less effectively.
Shorter Lifespan
Thin-film panels typically have a shorter lifespan, ranging from 10 to 20 years, making them less durable and requiring more frequent replacements compared to crystalline silicon panels.
Space Requirements
Due to their lower power output per square meter, thin-film panels may require more installation space to achieve comparable power production to crystalline silicon panels.
Technological Advancements Needed
Ongoing research is needed to enhance the efficiency of thin-film panels to make them more competitive with other solar technologies in terms of power output.
How do thin-film solar panels work?
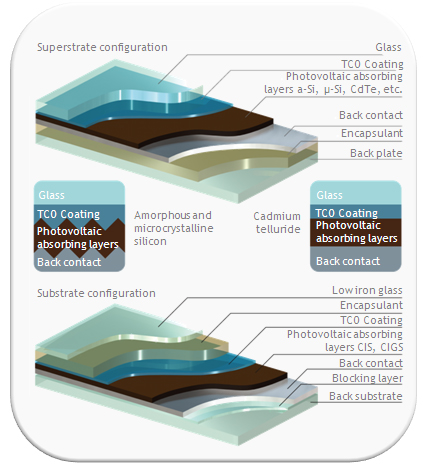
Thin-film solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect.
Unlike traditional crystalline silicon panels, which use rigid silicon wafers, thin-film panels employ a different construction method using thin layers of semiconductor materials.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how thin-film solar panels work:
Layered Structure
Thin-film solar panels consist of several layers, typically deposited onto a substrate such as glass, plastic, or metal. The key semiconductor materials include amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS).
1. Absorption of Sunlight
When sunlight hits the semiconductor layers, the energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the semiconductor material. Each type of semiconductor material has a unique ability to absorb specific wavelengths of light.
2. Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs
The absorbed energy excites electrons within the semiconductor material, creating electron-hole pairs. This process is crucial for generating an electric current.
3. Electric Current Flow
The excited electrons create a flow of electric current. Thin-film panels have electrodes connected to the semiconductor layers, allowing the generated electric current to be captured and directed for external use.
4. Conversion to Usable Electricity
The captured electric current is then directed through the panel’s electrical circuit to an inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), suitable for powering homes, businesses, or the electric grid.
Which is better thin-film or monocrystalline solar panel?
The choice between thin-film and monocrystalline solar panels depends on specific project requirements and priorities.
Here’s a comparison to help you decide:
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Advantages
- Cost-Effectiveness: Thin-film panels are generally more cost-effective to produce, making them suitable for large-scale installations where initial investment is crucial.
- Flexibility: The thin and flexible nature of these panels allows for versatile installations on curved surfaces or irregular shapes.
- Rapid Manufacturing: Thin-film technology is the fastest and easiest to manufacture among solar panel types.
Disadvantages
- Lower Efficiency: Thin-film panels typically have lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels, resulting in a lower power output per square meter.
- Shorter Lifespan: The lifespan of thin-film panels is generally shorter, ranging from 10 to 20 years.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Advantages
- High Efficiency: Monocrystalline panels are known for their high efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity, providing a higher power output.
- Compact Design: Monocrystalline panels offer higher power density, making them suitable for installations where space is limited.
Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: Monocrystalline panels are typically more expensive to produce than thin-film panels, impacting the initial investment.
- Rigid Structure: The rigid design of monocrystalline panels limits installation options to flat surfaces.
Choosing Between Them
- Consider Space: If space is abundant and cost-effectiveness is a priority, thin-film panels might be suitable.
- For limited space and a higher budget, monocrystalline panels could be a better choice.
- For limited space and a higher budget, monocrystalline panels could be a better choice.
- Installation Requirements: Thin-film panels offer more flexibility in installation, making them suitable for unique architectural applications.
- Monocrystalline panels are rigid and best suited for flat surfaces.
- Monocrystalline panels are rigid and best suited for flat surfaces.
- Efficiency vs. Cost: If maximizing efficiency is critical, and the budget allows, monocrystalline panels may be the preferred option.
- If cost-effectiveness is a priority and the space is available, thin-film panels could be a more suitable choice.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the specific needs, budget, and available space for each project.
Are thin-film solar panels worth it?

Cost Consideration
Thin-film solar panels are priced between $0.75 and $1.10 per watt.
That makes a 7.5kWh system (able to power an average American household) cost $5600 to $8250, excluding installation (approx. $6,000 – $8,000).
Comparing this with the national average cost of a 7.5 kW system, ranging from $18,750 to $26,250, with most homeowners spending around $22,500 (source), thin-film seems cost-effective.
If you’re interested as to how many solar panels you need to power your house check out our helpful guide here.
Low-Cost Systems Consideration
However, thin-film and polycrystalline panels, considered low-cost systems, present challenges: they are less space-efficient, less durable, and usually come with shorter warranties.
Given their space requirements, roof-mounting on houses is not recommended, particularly for residential installations.
So, that begs the question:
Are thin-film solar panels any good?
Yes, they can be.
Let’s not be too hard on thin-film panels because they can hold their ground in different settings! Despite not being a viable option for residential use, there are other cases where thin film solar panels can indeed shine:
Large Ground-Mounted Installations and Remote Areas
Thin-film panels shine in expansive ground-mounted solar projects and remote locations.
Their cost-effectiveness in large spaces compensates for lower efficiency, making them practical for off-grid settings.
Temporary Installations or Events
Lightweight and portable, thin-film panels are ideal for temporary installations, events, or emergency response situations, providing quick deployment and ease of transportation.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Thin-film’s flexibility makes it suitable for Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV), where they can be integrated into architectural elements like windows, facades, or roofing materials.
Experimental and Research Projects
Thin-film panels are preferred in experimental or research projects, offering adaptability for innovative applications and specialized environments where flexibility is prioritized over maximum efficiency.
FAQs About Thin-Film Solar Panels

How do thin-film solar panels differ from traditional solar panels?
Thin-film panels use a different construction method, employing layers of semiconductor materials on a substrate.
This makes them more flexible and lightweight compared to traditional crystalline silicon panels.
What types of semiconductor materials are used in thin-film solar panels?
Common semiconductor materials in thin-film panels include amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS).
Are thin-film solar panels less efficient than traditional panels?
Yes, thin-film panels generally have lower efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity compared to crystalline silicon panels.
However, they offer other advantages, such as cost-effectiveness and flexibility.
Can thin-film solar panels be installed on curved surfaces or irregular shapes?
Yes, the thin and flexible nature of these panels allows for versatile installations on curved surfaces or irregular shapes, making them suitable for unique architectural applications.
How long do thin-film solar panels last?
The lifespan of thin-film panels typically ranges from 10 to 20 years.
While they may have a shorter lifespan compared to crystalline silicon panels, their cost-effectiveness and specific applications make them a viable choice for certain projects.
Can you walk on thin-film solar panels?
Generally, it is not recommended to walk on thin-film solar panels.
They are more delicate than traditional panels, and walking on them can damage the semiconductor layers and reduce their effectiveness.
It’s advisable to follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance and avoid direct pressure on the panels.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our journey through the realm of thin-film solar panels, you’ve gained insights into their science, applications, and considerations.
The world of renewable energy holds boundless possibilities, and thin-film panels, with their sleek design and flexibility, offer a unique contribution.
If you have sufficient space and are in search of a cost-effective solar option, thin film panels might align perfectly with your needs. Their flexibility and affordability make them a compelling choice for those eager to step into a greener, more sustainable future.
Ready to make a solar choice tailored to your space and budget? Your journey begins now.