What exactly are sustainable dyes? How do they differ from conventional options? Are they as vibrant and diverse?
Fear not, curious reader! We are here to tell you all about eco-friendly colors that are to dye for.
What are sustainable dyes? (What are eco-friendly dyes?)

Sustainable Dye Definition:
A sustainable dye refers to a coloring agent used in textiles that is derived from eco-friendly sources, produced with minimal environmental impact, and exhibits characteristics such as biodegradability, reduced water usage, and avoidance of harmful chemicals.
These dyes contribute to more responsible and environmentally conscious practices in the textile and fashion industries.
Are sustainable dyes as vibrant as conventional dyes?
Absolutely! Sustainable dyes have evolved to match and even rival the vibrancy of conventional dyes.
Innovations in eco-friendly dyeing techniques and formulations have led to a broad spectrum of vivid colors, ensuring that fashion remains vibrant while minimizing environmental impact.
Key Points:
- Advanced Formulations:
- Sustainable dye formulations now incorporate advanced technologies, delivering intense and diverse color options.
- Specialized Techniques:
- Techniques such as digital printing with eco-friendly inks allow for precise color application, enhancing vibrancy.
- Natural Pigments:
- Natural plant-based dyes harness the rich pigments found in botanical sources, offering a vibrant and earth-friendly color palette.
- Innovative Processes:
- Techniques like plant-based indigo dyeing provide vibrant hues through traditional yet sustainable processes.
- Consumer Demand:
- Growing consumer demand for sustainable fashion has prompted the industry to prioritize both eco-consciousness and vibrant aesthetics.
Examples of Sustainable Dyes
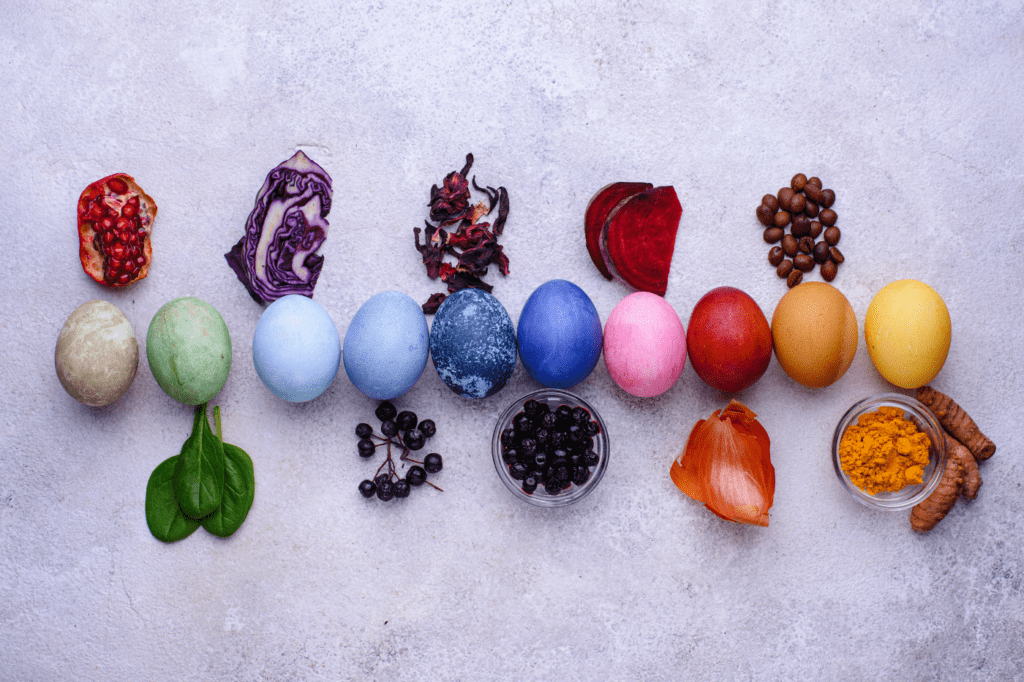
1. Natural Plant-Based Dyes:
- Derived From: Plants like indigo, turmeric, and madder.
- Process: Extracting color from plant parts like leaves, roots, or bark.
- Benefits: Eco-friendly, low environmental impact, biodegradable, and renewable.
2. Organic Dyes:
- Source: Extracted from organically grown plants or produced through eco-friendly chemical processes.
- Benefits: Reduced use of synthetic chemicals, promoting soil health in organic farming.
3. Low-Impact Synthetic Dyes:
- Characteristics: Engineered to minimize environmental impact.
- Benefits: Use less water and energy, and generate fewer toxic by-products compared to conventional synthetic dyes.
4. Water-Based Dyes:
- Base: Water serves as the primary solvent for the dye.
- Benefits: Lower VOC emissions, reduced use of hazardous chemicals, and easier waste treatment.
5. Recycled Water Dyeing:
- Method: Reusing water from dyeing processes, minimizing fresh water consumption.
- Benefits: Conservation of water resources, reducing overall environmental footprint.
6. Plant-Based Indigo Dyeing:
- Derived From: Indigofera plants.
- Traditional Method: Fermentation of the indigo plant leaves.
- Benefits: Biodegradable, energy-efficient, and a centuries-old sustainable practice.
7. Biodegradable Dyes:
- Characteristics: Break down naturally over time.
- Benefits: Reduce environmental impact and contribute to a circular, sustainable system.
8. Zero-Waste Dyeing Techniques:
- Approach: Minimizing or eliminating dye waste during the coloring process.
- Benefits: Drastically reduces pollution, creating a more sustainable dyeing process.
9. Non-Toxic and Azo-Free Dyes:
- Features: Absence of harmful chemicals, particularly azo compounds.
- Benefits: Safe for both the environment and human health.
10. Digital Printing with Eco-Friendly Inks:
- Process: Directly applying color to fabric through digital printing methods.
- Benefits: Reduces water usage, minimizes waste, and allows for precise color application.
Why are eco-friendly dyes important?

For a more in-depth exploration of the pros and cons of sustainable dyes check out our blog post here.
The Significance of Eco-Friendly Dyes
- Reduced Environmental Impact:
- Less Pollution: Eco-friendly dyes often involve processes that generate fewer toxic by-products, minimizing pollution of air and water compared to conventional dyeing methods.
- Conservation of Resources:
- Water Savings: Many eco-friendly dyeing techniques require less water, contributing to the conservation of this precious resource, especially crucial in regions facing water scarcity.
- Safe for Workers and Consumers:
- Human Health: Avoiding harmful chemicals in eco-friendly dyes ensures the well-being of both textile industry workers and consumers who come into contact with dyed products.
- Biodiversity Preservation:
- Natural Sources: Eco-friendly dyes derived from plants or other natural sources promote biodiversity conservation by reducing dependence on synthetic, environmentally impactful materials.
- Promotion of Sustainable Agriculture:
- Organic Farming: Dyes sourced from organically grown plants encourage sustainable agricultural practices, minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Low-Impact Processes: Techniques like low-impact synthetic dyeing or digital printing with eco-friendly inks often require less energy compared to traditional dyeing methods, contributing to overall energy efficiency.
- Circular Economy Support:
- Biodegradability: Eco-friendly dyes that are biodegradable contribute to the development of a circular economy, where products and materials can be safely returned to the environment without causing harm.
- Compliance with Regulations:
- Legal Standards: The use of eco-friendly dyes aligns with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and standards, ensuring that businesses operate within legal frameworks.
- Consumer Demand and Brand Reputation:
- Market Trends: With the rise of eco-conscious consumers, brands incorporating eco-friendly dyes meet market demands and build a positive reputation for environmental responsibility.
- Long-Term Sustainability:
- Preserving Ecosystems: By adopting eco-friendly dyeing practices, industries contribute to the overall sustainability of ecosystems, fostering a harmonious relationship between human activities and the environment.
In essence, eco-friendly dyes play a crucial role in fostering a more sustainable, ethical, and environmentally conscious approach within the textile and fashion industries, addressing pressing ecological challenges.
What are harmful dyes?
Harmful Dyes:
Harmful dyes refer to coloring agents used in textile processes that pose environmental and health risks due to their production methods, chemical composition, and potential long-term effects.
These dyes often involve synthetic chemicals and unsustainable practices.
The correlation between harmful dyes and the fast fashion industry is notable, as the demand for quick, inexpensive clothing often leads to the use of synthetic fabrics that require extensive dyeing processes with these harmful chemicals.
What is different about the eco-friendly dyeing processes?
Several crucial differences distinguish eco-friendly dyeing processes from traditional methods:
- Chemical Composition:
- Eco-Friendly Dyes: Primarily derived from natural sources or engineered with reduced environmental impact.
- Harmful Dyes: Often involve synthetic chemicals and compounds with higher toxicity levels.
- Production Methods:
- Eco-Friendly Dyes: Processes aim to minimize waste, water usage, and energy consumption.
- Harmful Dyes: Conventional dyeing methods may generate significant waste, contribute to water pollution, and require substantial energy.
- Water Usage:
- Eco-Friendly Dyes: Many eco-friendly techniques use less water, addressing concerns about the excessive consumption associated with traditional dyeing.
- Harmful Dyes: Traditional dyeing processes can be water-intensive, contributing to water scarcity issues.
- Biodegradability:
- Eco-Friendly Dyes: Emphasize biodegradability, ensuring that the dyes break down naturally without causing long-term harm.
- Harmful Dyes: Some synthetic dyes are not easily biodegradable, leading to persistent environmental pollution.
- Health and Safety:
- Eco-Friendly Dyes: Aim to minimize harm to human health, both for workers in the textile industry and consumers.
- Harmful Dyes: Exposure to certain harmful dye chemicals can pose health risks, ranging from skin irritation to more severe conditions.
Is dye bad for the environment?
Yes, conventional dyeing processes using harmful dyes can have detrimental effects on the environment:
- Harmful Environmental Impact:
- Harmful Dyes: Conventional dyeing processes can contribute to environmental degradation through water pollution, soil contamination, and depletion of natural resources.
- Long-Term Consequences:
- Persistent Pollution: Some harmful dyes may persist in the environment, leading to long-term ecological consequences.
- Resource Depletion:
- Water and Energy Use: Traditional dyeing methods often consume significant amounts of water and energy, contributing to resource depletion and environmental stress.
- Biodiversity Concerns:
- Habitat Impact: The environmental impact of harmful dyes can extend to ecosystems, potentially affecting biodiversity and disrupting natural habitats.
In summary, harmful dyes present multifaceted environmental challenges, while eco-friendly dyeing processes strive to mitigate these issues through sustainable practices and reduced ecological impact.
Rating Sustainable Dyes

1. Natural Plant-Based Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Natural Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: Derived from plants, natural dyes are renewable, biodegradable, and often involve traditional, low-impact extraction methods.
2. Organic Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Organic Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: Sourced from organically grown plants or produced through eco-friendly processes, organic dyes contribute to sustainable agriculture and reduced chemical use.
3. Low-Impact Synthetic Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Low-Impact Synthetics?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: Moderate to High
- Rationale: Engineered to minimize environmental impact, these dyes use less water and energy compared to conventional synthetic dyes.
4. Water-Based Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Water-Based Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: Water serves as the primary solvent, reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, hazardous chemical use, and facilitating easier waste treatment.
5. Recycled Water Dyeing:
How Sustainable Is Recycled Water Dyeing?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: By reusing water from dyeing processes, this technique minimizes fresh water consumption, contributing to overall water conservation.
6. Plant-Based Indigo Dyeing:
How Sustainable Is Plant-Based Indigo Dyeing?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: Derived from indigofera plants, this traditional method is energy-efficient, biodegradable, and has been a sustainable practice for centuries.
7. Biodegradable Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Biodegradable Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: These dyes break down naturally over time, contributing to a circular, sustainable system.
8. Zero-Waste Dyeing Techniques:
How Sustainable Are Zero-Waste Dyeing Techniques?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: By minimizing or eliminating dye waste, these techniques drastically reduce pollution and contribute to a more sustainable dyeing process.
9. Non-Toxic and Azo-Free Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Non-Toxic Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: High
- Rationale: With the absence of harmful chemicals, these dyes are safe for both the environment and human health.
10. Digital Printing with Eco-Friendly Inks:
How Sustainable Is Digital Printing?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: Moderate to High
- Rationale: Reducing water usage, minimizing waste, and allowing for precise color application, digital printing with eco-friendly inks is a more sustainable alternative.
These eco-friendly dye alternatives collectively contribute to a more sustainable and responsible approach within the textile and fashion industries.
BONUS
11. Reactive Dyes:
How Eco-Friendly Are Reactive Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: Moderate
- Rationale: While reactive dyes are widely used and offer good color fastness, they do require water-intensive processes and can contribute to pollution if not managed properly.
12. Acid Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Acid Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: Low to Moderate
- Rationale: Acid dyes typically have a higher environmental impact due to their use of toxic compounds. Efforts are made to manage and treat wastewater to mitigate their effects.
13. Pigment Dyes:
How Sustainable Are Pigment Dyes?
- Eco-Friendly Rating: Moderate
- Rationale: Pigment dyes can be eco-friendly as they often do not require additional chemicals for fixation. However, some formulations may still contain harmful additives, impacting their overall sustainability.
These additional dye types have varying degrees of eco-friendliness, highlighting the importance of considering the environmental impact of each dyeing method within the broader context of sustainable practices in the textile industry.
How do you make sustainable dyes?
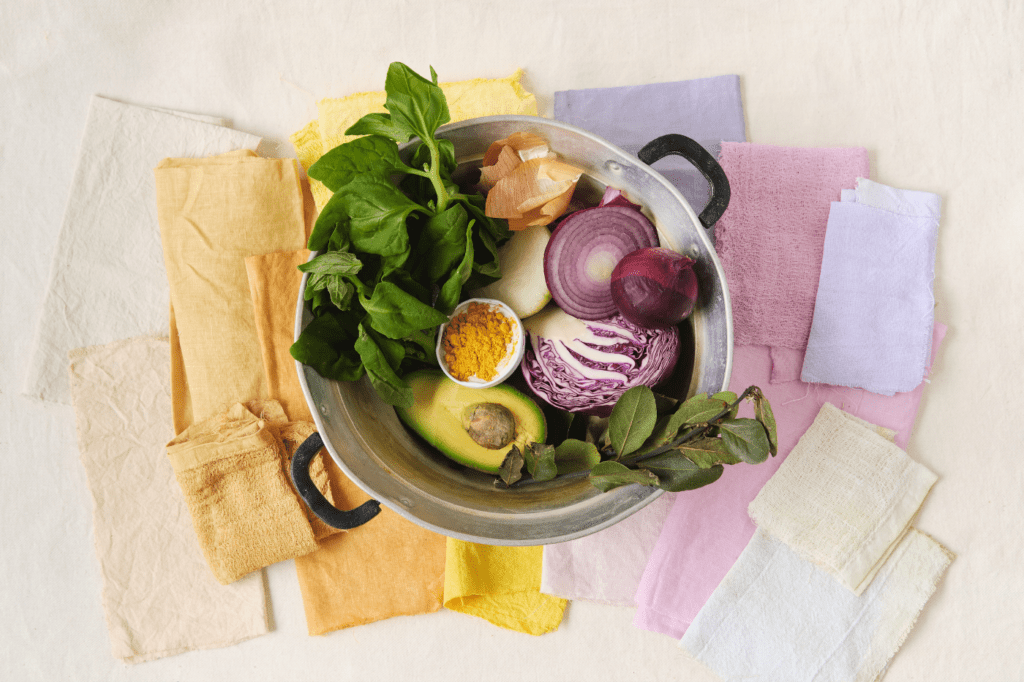

Crafting sustainable dyes at home is a fun activity that aligns with eco-conscious practices. Follow this step-by-step tutorial to get started with sustainable dyeing:
Materials Needed:
- Plant-based materials (e.g., onion skins, avocado pits, or spinach)
- Water
- Stainless steel or enamel pot
- Fabric or material to dye
- Strainer
- Mason jars or containers
Procedure:
- Prepare Your Fabric:
- Ensure the fabric is clean and pre-washed for better dye absorption.
- Select Your Dye Source:
- Choose plant-based materials rich in natural pigments. For example, onion skins can yield warm tones, while avocado pits offer subtle pinks.
- Extract Dye Pigments:
- In a stainless steel or enamel pot, cover your chosen dye source with water. Simmer the mixture until the water takes on the desired color.
- Strain the Dye Bath:
- Remove plant particles by straining the liquid, leaving you with a smooth dye bath.
- Prepare Your Fabric for Dyeing:
- Wet the fabric and place it in the dye bath, ensuring even coverage.
- Dyeing Process:
- Simmer the fabric in the dye bath for an extended period, allowing the natural pigments to infuse the material.
- Rinse and Dry:
- Once the desired color is achieved, rinse the fabric thoroughly, and let it air-dry.
Benefits of Homemade Sustainable Dyes:
- Environmentally Friendly: Utilizing plant-based materials reduces the environmental impact compared to conventional dyes.
- Customization: Experiment with different plant sources to create unique and personalized colors.
- Educational: Gain a deeper understanding of natural dye processes and their connection to sustainability.
Here’s an engaging tutorial to discover how to create natural dyes using ingredients like beets, red cabbage, and turmeric. Or learn the art of eco-printing with this detailed tutorial.
Conclusion
In closing, sustainable dyes aren’t just colors – they’re a commitment to a greener tomorrow.
Your Path:
- Choose Wisely: Opt for natural dyes to minimize environmental impact.
- Support Ethical Brands: Back those committed to eco-friendly dyeing.
- Spread Awareness: Educate others to amplify the positive impact.